https://app.codility.com/programmers/lessons/7-stacks_and_queues/stone_wall/
StoneWall coding task - Learn to Code - Codility
Cover "Manhattan skyline" using the minimum number of rectangles.
app.codility.com
문제
- 벽은 직선으로 N meter만큼 높고, 두께는 일정하지만, 다른 장소에 다른 높이를 가지고 있다.
- 벽의 높이 H배열은 N인 양수들로 이루어져 있다.
- H[I]는 I ~ I+1( 왼쪽 끝부터 오른쪽 끝 )의 벽의 높이를 뜻한다.( 자세히는 H[0]은 벽의 왼쪽 끝, H[N-1]은 벽의 오른쪽 끝의 높이를 의미한다. )
- 모든 벽들은 정육면체의 석재 블록들로 지어진다.
- 최소한의 벽돌의 개수를 구하라.
- 예시 :
given array H containing N = 9
integers: H[0] = 8 H[1] = 8 H[2] = 5 H[3] = 7 H[4] = 9 H[5] = 8 H[6] = 7 H[7] = 4 H[8] = 8
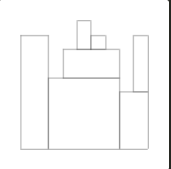
return 7
제한조건
- N is an integer within the range [1..100,000];
- each element of array H is an integer within the range [1..1,000,000,000].
N은 1 ~100,000 사이의 정수이다.
H 배열의 각각의 원소들은 1 ~ 1,000,000,000 사이의 수이다.
풀이
- 예제를 순서대로 하다보면 몇가지 로직이 보인다.
- Queue 자료 구조를 활용하도록 한다.
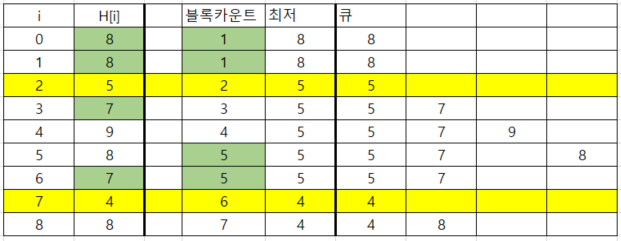
- 1 -> 2일 때, 현재 차례(2)의 높이 값보다 높은 큐안의 값들은 다 버린다, 이 때 큐가 다 비어있으면 count+1, 현재 차례의 높이 값을 큐안에 넣어준다.
- 2 -> 3일 때, H[3]= 7은 큐 안의 모든 높이 값보다 높다, 이 때는 count+1, 큐에 그 값을 넣어준다.( 3 -> 4 동일 )
- 4 -> 5일 때, H[5]=8은 큐 안의 모든 높이 값과 비교, 8보다 높은 9 제외하고 동일한 값이 있는지 비교 후, 없으면 count+1하고 큐에 그 값을 넣어준다.
- 5 -> 6일 때, H[6]=7은 (4 -> 5)와 동일한 로직으로 실행, 8을 제외시키고 동일한 값이 있는지 비교, 있으므로 no count후 넘어간다.
- 6 -> 7일 때, H[7]=4로 큐안의 모든 높이 값보다 작다. 따라서 모든 큐의 값을 버리고 현재의 값을 넣어주고 count+1한다.
- 7 -> 8일 때는 2 -> 3 넘어갈 때와 동일
- 위와 같이 따르면, queue.size() == 0 일 때는 queue에 값을 넣어주며 count + 1
- queue.size() != 0일 때, queue안의 높이 값이 현재 차례의 높이값과 비교 하여 높은 수는 다 버린다.
- queue를 모두 순회하고 queue가 비어 있으면( 현재 차례의 높이가 큐안의 높이 값보다 다 낮은 경우 ) 현재 차례의 높이 값을 큐에 넣고, count+1
- queue가 비어 있지 않다면, 동일한 값이 있는지 확인 후 동일한 값이 있으면 no count, 동일한 값이 없으면 count+1하고 큐에 현재의 값을 넣어준다.
예상 시간복잡도 : for문을 순회하고 그 안에서 queue도 순회하기 때문에 최악의 시간 복잡도는 O(N**2)..일 듯한데..
소스코드
// you can also use imports, for example:
import java.util.*;
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// System.out.println("this is a debug message");
class Solution {
public int solution(int[] H) {
// write your code in Java SE 8
if( H.length < 2 ){
return 1;
}
int count = 0;
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for( int i:H ){
if( queue.size() == 0 ){
queue.add(i);
count++;
}else{
// queue 정리
for( int j=0; j<queue.size(); j++ ){
if( queue.peek() != null ){
int tmp = queue.poll();
if( i >= tmp ){
queue.add(tmp);
}
}
}
if( queue.size() == 0 ){
queue.add(i);
count++;
}else{
if( !queue.contains(i) ){
queue.add(i);
count++;
}
}
}
}
return count;
}
}

Time out 에러와 잘못된 답을 도출하는..
결국 구글링..ㅠㅠ
https://romanticcode.tistory.com/37
[Codility] Stone wall
You are going to build a stone wall. The wall should be straight and N meters long, and its thickness should be constant; however, it should have different heights in different places. The height of..
romanticcode.tistory.com
stack으로 풀어도 되는 부분;
- stack으로 풀게 되면서 현재 차례의 높은 값만 stack에 저장
- LIFO 구조 이므로 가장 높은값이 제일 윗부분에 존재하므로 모든 stack을 다 순회 안해도되게 됨...( queue는 반대로 모두 순회하게 되는.. 양방향 queue면 모를까; )
// you can also use imports, for example:
import java.util.*;
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// System.out.println("this is a debug message");
class Solution {
public int solution(int[] H) {
// write your code in Java SE 8
if( H.length < 2 ){
return 1;
}
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
int count = 0;
for( int i:H ){
// stack의 제일 윗부분을 빼서 비교하는 로직
while( !stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() > i ){
stack.pop();
}
if( stack.isEmpty() || stack.peek() < i ){
stack.push(i);
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
}

난이도 easy도 easy하지 않다..ㅠ
Deque로 구현한 코드
// you can also use imports, for example:
import java.util.*;
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// System.out.println("this is a debug message");
class Solution {
public int solution(int[] H) {
// write your code in Java SE 8
if( H.length < 2 ){
return 1;
}
int count = 0;
Deque<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for( int i:H ){
if( queue.size() == 0 ){
queue.add(i);
count++;
}else{
// deque 정리
// 마지막의 수가 제일 높은 수
while( queue.size() > 0 && queue.peekLast() > i ) {
queue.pollLast();
}
if( queue.size() == 0 ){
queue.add(i);
count++;
}else{
if( !queue.contains(i) ){
queue.add(i);
count++;
}
}
}
}
return count;
}
}

timeout 이슈가 발생한다... 왜?? -> deque에서 firstAdd와 lastAdd를 지정해서 넣어서 높은 수가 한쪽에 있게 해야하는데 위의 소스코드에서는 뒤죽박죽이여서 Queue를 다 순회하는 것과 같은 작업이 진행되어 Timeout 발생..
// you can also use imports, for example:
import java.util.*;
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// System.out.println("this is a debug message");
class Solution {
public int solution(int[] H) {
// write your code in Java SE 8
if( H.length < 2 ){
return 1;
}
int count = 0;
Deque<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
// Deque<Integer> deque = new LinkedList<>();
for( int i:H ){
while( queue.size() > 0 && queue.peekLast() > i ) {
queue.pollLast();
}
if( queue.size() == 0 || queue.peekLast() < i ){
queue.addLast(i);
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
}


'코딜리티 문제풀이' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Codility Lesson 08 - EquiLeader(JAVA) (0) | 2022.04.01 |
|---|---|
| Codility Lesson 08 - Dominator( JAVA ) (0) | 2022.04.01 |
| Codility Lesson 07 - Nesting( JAVA ) (0) | 2022.03.30 |
| Codility Lesson 07 - Fish( JAVA ) (0) | 2022.03.30 |
| Codility Lesson 07 - Brackets( JAVA ) (0) | 2022.03.29 |



